Very interesting analysis, I thought I’d pass it on. Al Assad's Last Stand is republished with permission of Stratfor.
By Omar Lamrani
The battle for Damascus is raging with increasing intensity while rebels continue to make substantial advances in Syria's north and east. Every new air base, city or town that falls to the rebels further underlines that Bashar al Assad's writ over the country is shrinking. It is no longer possible to accurately depict al Assad as the ruler of Syria. At this point, he is merely the head of a large and powerful armed force, albeit one that still controls a significant portion of the country.
The nature of the conflict has changed significantly since it began nearly two years ago. The rebels initially operated with meager resources and equipment, but bolstered by defections, some outside support and their demographic advantage, they have managed to gain ground on what was previously a far superior enemy. Even the regime's qualitative superiority in equipment is fast eroding as the rebels start to frequently utilize main battle tanks, infantry fighting vehicles, rocket and tube artillery and even man-portable air-defense systems captured from the regime's stockpiles.
Weary and stumbling, the regime is attempting to push back rebel forces in and near Damascus and to maintain a corridor to the Alawite coast while delaying rebel advances in the rest of the country. Al Assad and his allies will fight for every inch, fully aware that their power depends on the ability of the regime forces to hold ground.
The Battle for Damascus
After the last surge in fighting around Damascus in July and August, the regime kept large numbers of troops in the area. These forces continued search and destroy operations near the capital despite the considerable pressure facing its forces in the rest of the country, including in Aleppo. Once the rebels began to make gains in the north and east, the regime was forced to dispatch some of its forces around Damascus to reinforce other fronts. Unfortunately for the regime, its operations in the capital area had not significantly degraded local rebel forces. Rebels in the area began intensifying their operations once more, forcing the regime to recall many of its units to Damascus.It is important to remember that, despite considerable setbacks, al Assad's forces still control a sizable portion of Syria and its population centers. After failing to take Damascus in Operation Damascus Volcano in July, the rebels are again stepping up their efforts and operations in the Damascus area. However, unlike in their previous failed operation, this time the rebels are relying on an intensive guerrilla campaign to exhaust and degrade al Assad's substantial forces in Damascus and its countryside.
Aware of the magnitude of the threat, the regime has reportedly shifted its strategy in the battle for Damascus to isolating the city proper from the numerous suburbs. The rebels have made considerable headway in the Damascus suburbs. For example, on Nov. 25 rebels overran the Marj al-Sultan military air base in eastern Ghouta, east of the capital. Rebel operations in the outskirts of Damascus have also interrupted the flow of goods to and from the city, causing the prices of basic staples such as bread to skyrocket.
Rebel Gains in the East and North
Damascus is not the only area where the regime is finding itself under considerable pressure. The rebels have made some major advances in the last month in the energy-rich Deir el-Zour governorate to the east. Having seized a number of towns, airfields and military bases, the rebels have also taken the majority of the oil fields in the governorate. They captured the Al-Ward oil field Nov. 4, the Conoco natural gas reserve Nov. 27 and, after al Assad's forces withdrew from it on Nov. 29, the Omar oil field north of the town of Mayadeen. Al Assad's forces now control only five oil fields, all located west of the city of Deir el-Zour. With the battle for the city and its associated airfield intensifying, even those remaining fields are at risk of falling into rebel hands.
The rebel successes in Deir el-Zour have effectively cut the regime's ground lines of communication and supply to Iraq. They have also starved the regime of the vast majority of its oil revenue and affected its ability to fuel its war machine. At the same time, the rebels are reportedly already seeking to capitalize on their seizure of the eastern oil fields. According to reports, the rebels are smuggling oil to Turkey and Iraq and using the revenue to purchase arms. They are also reportedly using the oil and natural gas locally for power generators and fuel.
While all of eastern Syria may soon fall into rebel hands, rebels in the north have continued to isolate al Assad forces in Idlib and Aleppo governorates, particularly in the capital cities of those two provinces. After overrunning the 46th regiment near Atarib on Nov. 19 following a two-month siege, the rebels are now looking to further squeeze remaining regime forces in Aleppo by taking the Sheikh Suleiman base north of the 46th regiment's former base.
The Rebels' Improved Air Defense Capability
Isolated and surrounded, regime forces in the north are increasingly relying on air support for both defense and supply. However, this advantage is deteriorating every day and is increasingly threatened by the rebels' improved air defense arsenal and tactics.
The rebels first attempted to acquire air defense weaponry by seizing heavy machine guns and anti-aircraft artillery. They captured a number of air defense bases, taking 12.7 mm DShK heavy machine guns, 14.5 mm KPV heavy machine guns and even 23 mm ZU-23-2 autocannons. Over time, the rebels became more proficient with these weapons, and an increasing number of Syrian air force fixed-wing and rotary aircraft were shot down. The rebels also formed hunter-killer groups with air defense equipment mounted on flatbed trucks that provided them mobile platforms for targeting regime air and infantry units.
As more and more regime bases were taken, the rebels were able to bolster their air defense equipment through the capture of a number of man-portable air-defense systems. At the outset of the conflict, the Syrian military maintained a large inventory of shoulder-fired air-defense missiles, likely thousands of missiles ranging from early generation SA-7s to very advanced SA-24s. These missiles were stored in army bases across the country. There are also unconfirmed reports that Qatar and Saudi Arabia may have transferred some man-portable air-defense systems to the rebels through Turkey.
The rebels tallied their first confirmed kill with shoulder-fired air-defense missiles Nov. 27, when they shot down a Syrian Arab Air Force Mi-8/17 helicopter near Aleppo city. The weapon system used in the attack was likely an SA-7, SA-16 or SA-24 captured from the 46th regiment. The surface-to-air missiles are a serious upgrade in the rebels' air defense capability.
The Fight Continues
Having isolated al Assad's forces in the north and made substantial advances in the east, the rebels are poised to push farther into the Orontes River Valley to relieve the beleaguered rebel units in the Rastan, Homs and al-Qusayr areas of Homs governorate. For months, regime forces have sought to overwhelm the remaining rebel forces in Homs city, but the rebels have managed to hold out. The rebels are also set to begin pushing south along the main M5 thoroughfare to Khan Sheikhoun and the approaches to Hama. However, first they need to overwhelm the remaining regime forces in Wadi al-Dhaif near Maarrat al-Numan.
Alternatively, the regime is fighting hard to maintain its control over the Orontes River Valley around Homs in order to keep an open corridor linking Damascus to the mostly Alawite coast. Not only is this corridor at risk of eventually being cut off, but the regime is also facing a substantial push by rebel forces into northeastern Latakia governorate from Idlib. Rebels have advanced in the vicinity of the Turkman Mountain, have taken control of Bdama and are now fighting their way down in the direction of Latakia city.
While events in Damascus and Rif Damascus are increasingly worrisome for the regime, al Assad's forces in the rest of Syria are also under considerable pressure from rebel advances. It is by no means certain that al Assad's forces are under imminent threat of collapse because they still hold a great deal of territory and no major city has yet been completely taken by the rebels. The retreat and consolidation of al Assad's forces also allows them to maintain shorter and less vulnerable lines of supply. However, it is clear that the regime is very much on the defensive and has been forced to gradually contract its lines toward a core that now encompasses Damascus, the Orontes River Valley and the mostly Alawite coast. With the regime's situation rapidly deteriorating, even the attempt to stage a gradual withdrawal to the core is risky.


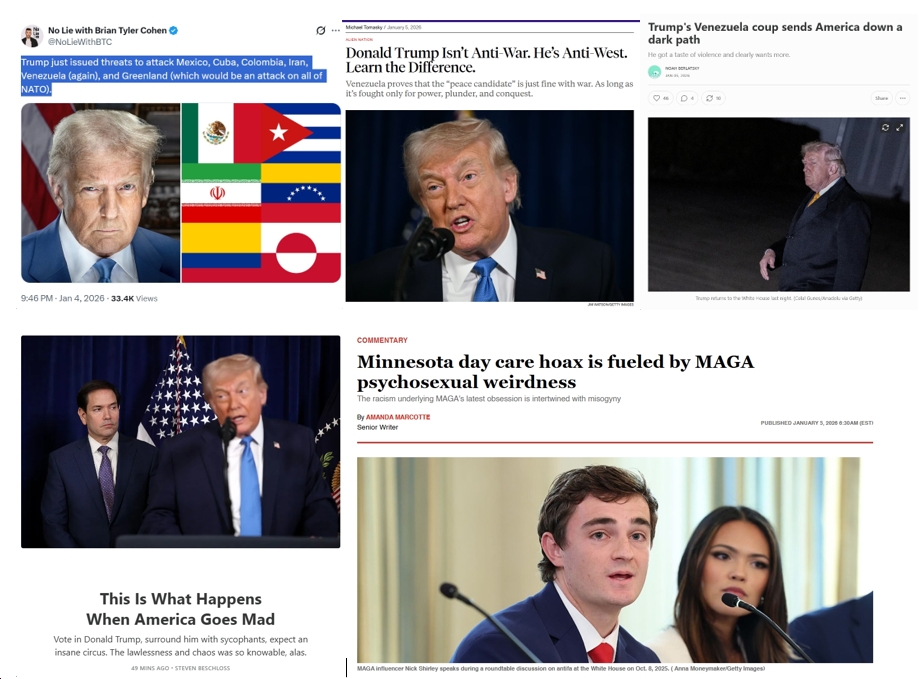
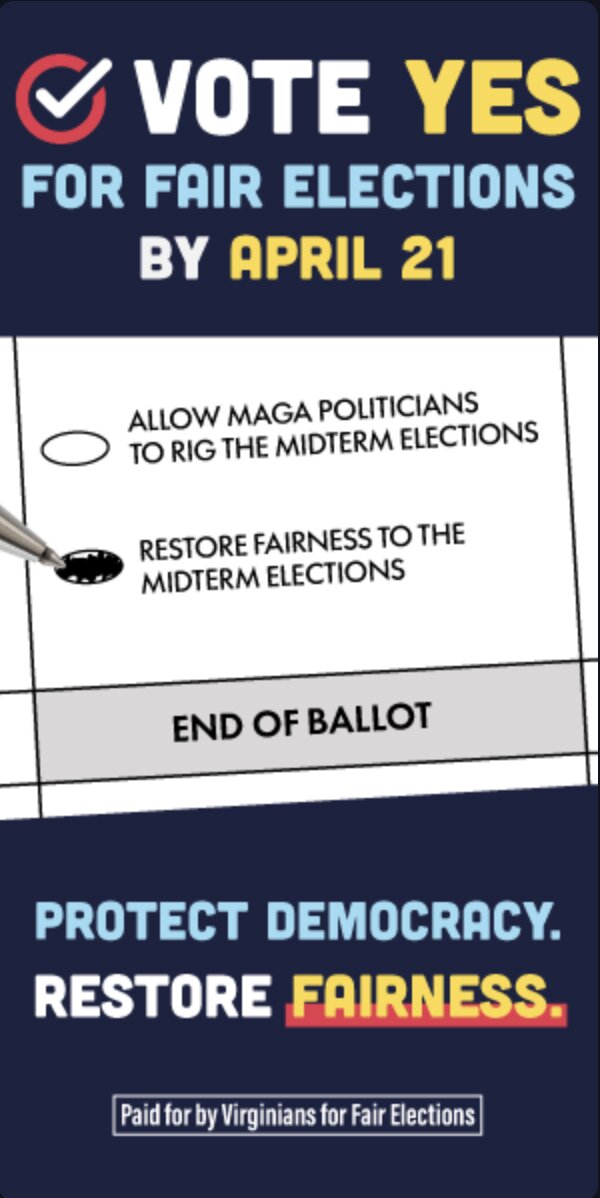
![Sunday News: “Trump Is Briefed on Options for Striking Iran as Protests Continue”; “Trump and Vance Are Fanning the Flames. Again”; “Shooting death of [Renee Good] matters to all of us”; “Fascism or freedom? The choice is yours”](https://bluevirginia.us/wp-content/uploads/2026/01/montage011126.jpg)
![Thursday News: “Europe draws red line on Greenland after a year of trying to pacify Trump”; “ICE Agent Kills Woman, DHS Tells Obvious, Insane Lies About It”; “Trump’s DOJ sued Virginia. Our attorney general surrendered”; “Political domino effect hits Alexandria as Sen. Ebbin [to resign] to join Spanberger administration”](https://bluevirginia.us/wp-content/uploads/2026/01/montage010826.jpg)
![New Year’s Day 2026 News: Full Video of Jack Smith Testimony – “The attack that happened at the Capitol…does not happen without [Trump]”; Trump/RFK Jr Make Measles Great Again; Right-Wing YouTuber Nick Shirley Definitely Not a Real Journalist; Musk Did Enormous Damage in 2025](https://bluevirginia.us/wp-content/uploads/2026/01/montage010126.jpg)