by Ivy Main, cross posted from Power for the People VA
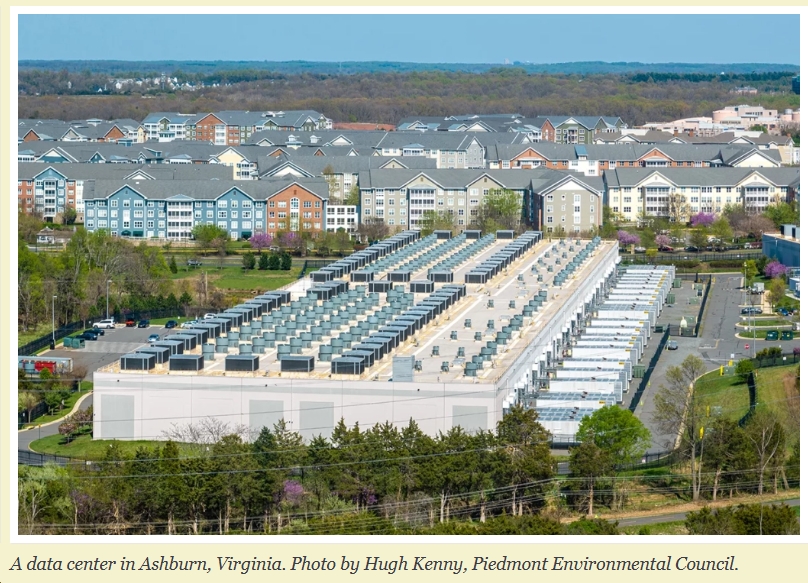
Amazon Web Services jump-started the utility solar industry in Virginia in 2015, when it announced plans for its first solar farm in Accomack County. Three years later, Amazon remains the biggest purchaser of solar in the commonwealth, allowing it to offset some of the enormous amount of energy used by its data centers.
Yet the company’s energy footprint in Virginia far exceeds the energy output of its solar projects. The addition of a new headquarters in Arlington will further increase its need for electricity, and will attract new residents who will also use electricity. All this demand poses a problem for the company and the climate: Dominion Virginia Power will burn more coal and fracked gas to meet Amazon’s energy need, unless Amazon acts to ensure the power comes from renewable sources.
Like many big tech companies, Amazon has adopted aggressive sustainability goals, including a “long-term commitment to achieve 100% renewable energy usage” for its data centers. But the details of its commitment are fuzzy, and the qualifier “long-term” makes the commitment meaningless.
Earth to Jeff Bezos: in the “long term” climate change will put HQ2 under water.
If Amazon still wants a habitable planet to compete in, it should consider the entire energy footprint of its operations, and make sure it is meeting these needs 24/7 with clean, renewable energy. Solar should be a big part of the plan, but so should land-based wind and offshore wind, which complement solar by providing power in the evening and at night. An investment in battery storage would round out the package nicely.
Virginia officials made a perfunctory mention of renewable energy availability to Amazon in the state’s bid package (see page 184). This was accompanied by a quote from Bob Blue of Dominion Energy, promising to sell the company renewable energy. (Be pleased, Mr. Bezos; that’s not a promise he’s made to the rest of us.)
Arlington County has reportedly discussed with Amazon how to make its new campus as environmentally-friendly as possible. Arlington is considering making a commitment to 100 percent renewable energy by 2035, so it has a real incentive to ensure that newcomers are part of the solution, not part of the problem.
Given today’s building technology, there is no reason the National Landing campus should not set a new standard for energy-efficient design. Ideally that will include on-site solar as well. Local officials also want to see enough improvements to transit, pedestrian and biking routes to keep 25,000 new commuters from spewing air pollution while they sit in traffic.
Even if Amazon and Arlington do everything right, though, the campus will need to purchase electricity from off-site generation—and there is still the matter of those power-hungry data centers.
Amazon can take Bob Blue up on his offer and let Dominion supply the company with all the renewable energy it needs. Caveat emptor, though: Dominion’s idea of renewable energy includes resources of dubious value to the climate, like the burning of trash and woody biomass.
And, thanks largely to Dominion’s clout in the General Assembly, Virginia has many barriers to on-site solar, which limit customers’ ability to supply their own renewable energy. We also boast a renewable portfolio standard that works approximately opposite to that of every other state, by ensuring wind and solar will never be part of our resource mix.
Come to think of it, we could really use Amazon’s negotiating chops with our legislators.
In any case, with or without Dominion’s help, Amazon will find plenty of opportunities to procure wind as well as more solar in Virginia. Apex Clean Energy’s Rocky Forge wind farm near Roanoke is already permitted and ready for construction as soon as a customer shows up. Apex now has two additional wind farms in development in southwest Virginia—a nice way to support areas of the state outside of Northern Virginia.
Offshore wind is another opportunity to deliver energy at scale while supporting jobs in the Hampton Roads region. Although offshore wind is poised to become a huge industry in the U.S. within the next ten years, right now only the northeastern states are moving forward with offshore wind farms in the near term. Amazon could make it happen here, too.
Dominion Energy has secured approval for two test turbines off the Virginia coast, but the utility has been slow-walking plans to develop hundreds more turbines in the commercial lease area it owns the rights to. In part that’s because Dominion doesn’t see how to get the State Corporation Commission (SCC) to approve the cost to ratepayers.
That wouldn’t be an issue if Amazon were the buyer, but nor is Amazon limited to Dominion as a supplier of offshore wind. Amazon could let Dominion and its developer, Ørsted, compete against Avangrid, the developer that holds the lease on the Kitty Hawk offshore wind area just over the border in North Carolina. The power from both areas has to come to shore at the same point in Virginia Beach, where a high-voltage transmission line is available. Avangrid has already announced that it is speeding up its development work in hopes of appealing to Virginia customers.
It will take several years for Amazon to build out HQ2, but given how much electricity the company already uses in Virginia, there is no reason to wait on making new investments in renewable energy. Virginians, and the planet, will thank you.
This post first appeared in the Virginia Mercury on November 26, 2018.


![Sunday News: “Trump Is Briefed on Options for Striking Iran as Protests Continue”; “Trump and Vance Are Fanning the Flames. Again”; “Shooting death of [Renee Good] matters to all of us”; “Fascism or freedom? The choice is yours”](https://bluevirginia.us/wp-content/uploads/2026/01/montage011126.jpg)
![VA DEQ: “pollution from data centers currently makes up a very small but growing percentage of the [NoVA] region’s most harmful air emissions, including CO, NOx and PM2.5”](https://bluevirginia.us/wp-content/uploads/2026/01/noxdatacenters.jpg)
![Thursday News: “Europe draws red line on Greenland after a year of trying to pacify Trump”; “ICE Agent Kills Woman, DHS Tells Obvious, Insane Lies About It”; “Trump’s DOJ sued Virginia. Our attorney general surrendered”; “Political domino effect hits Alexandria as Sen. Ebbin [to resign] to join Spanberger administration”](https://bluevirginia.us/wp-content/uploads/2026/01/montage010826.jpg)