( – promoted by lowkell)
Faith communities, colleges, schools, local governments and non-profits will find it easier to “go solar” under a law that takes effect in Virginia on July 1. Eligible customers will be able to install solar panels or wind turbines with little or no upfront cost, paying only for the electricity the systems provide. This arrangement, known as a third-party power purchase agreement (PPA), has been the driver for most of the solar projects in the U.S. in recent years, but prior to this year utilities had blocked its use in most of Virginia.
The new law creates a two-year pilot program allowing customers of Dominion Virginia Power to install projects as large as 1 megawatt (1,000 kilowatts) using PPAs financed by private companies. Projects must have a minimum size of 50 kilowatts, so the program can be used by many commercial customers but excludes homeowners, whose solar PV systems more typically fall in the 4-to-8 kilowatt size.
Importantly, however, the 50-kilowatt minimum does not apply to tax-exempt entities. PPAs are one of the only ways available for tax-exempt entities to benefit from the federal 30% tax credit for renewable energy systems; a tax-paying investor actually owns the system and uses the credits, passing along the savings to the customer. Thus the program could open up a new solar market in Virginia focused on what might be considered a natural vanguard for renewable energy: houses of worship, colleges, schools and nonprofits.
PPAs also offer an advantage over buying solar panels outright: even though the solar system is on the customer’s roof, someone else actually installs, owns and maintains it. That means less hassle for the customer and no upfront capital cost. The customer only has to pay for the solar power that’s produced. With prices for solar systems having fallen dramatically in recent years, customers will generally be able to buy solar energy under a PPA for no more than they now pay for power from non-renewable sources.
In states with incentive programs, including Maryland and DC, customers actually save money on their utility bills with solar PPAs. Virginia customers may not save money at first. Depending on the contract terms, however, customers may save money in future years, and can end up owning the solar system outright eventually, which will allow them to save quite a bit of money on electricity in the long run.
PPAs are the most common financing method for rooftop solar systems across the country. Companies like Solar City and Sungevity have created a profitable business model around financing and owning solar systems on customers’ property. Given the lack of state incentives in Virginia, Solar City isn’t expected to enter the market here. Financing PPAs in Virginia can still be profitable, but it presents challenges. Still, for people with cash sitting in CDs and bank accounts earning less than 1% interest, financing a solar project at their neighborhood church or school can be rewarding financially as well as spiritually.
One of the few companies with experience in Virginia PPAs is Secure Futures, LLC of Staunton, Virginia. CEO Tony Smith says his company’s business model is to “work with tax exempt entities to met their environmental, educational and thought leadership goals through solar installations that we own and operate in ways that deliver immediate operational savings and solid long term returns.”
The new law will involve rulemaking by Virginia’s regulatory body, the State Corporation Commission, to settle the details–including how the pilot program is tracked and how a qualifying customer applies for the limited kilowatts available over the two-year period. The SCC should be issuing a docket for a public hearing in the near future. Since many customers need months of lead-time, it’s not too soon to start the planning process.
Free workshops will offer information about solar PPAs beginning in June
On June 23 at 7 p.m., Greater Washington Interfaith Power and Light (GWIPL) and the Sierra Club will hold a free workshop for faith congregations at Mount Vernon Unitarian Church in Alexandria, one of the first Virginia churches to install solar panels. Representatives of solar companies including Secure Futures and Abakus Solar of Richmond, Virginia will be on hand to answer questions.
GWIPL has worked extensively with DC and Maryland congregations on similar solar projects and has compiled an informative booklet that can be downloaded from the gwipl.org website.
The Virginia Chapter of the Sierra Club supported the solar industry in its quest to open up the Virginia market for solar PPAs and believes churches and other faith communities can play a big role in making the benefits of renewable energy available to everyone.
Sierra Club and Virginia Interfaith Power and Light are also planning a June workshop for Richmond-area congregations. Similarly, Sierra Club and National Wildlife Federation, which has been working with community colleges on “green campus” projects, are planning a workshop designed especially for colleges and universities.
In addition to their target audiences, all workshops will be open to anyone who wants to learn more about the solar opportunity. For information, contact corrinabeall@sierraclub.org.
New law an imperfect compromise
The PPA legislation was a compromise between the solar industry and Dominion Power, which had sparred over the question of whether PPAs are legal in Virginia. When Secure Futures tried to install a system at Washington & Lee University in 2011 under a PPA, Dominion sent cease and desist letters claiming the arrangement was illegal. Eventually Secure Futures and the university used a different financing approach so the project could move forward.
Dominion also blocked a 2012 bill in the General Assembly that would have expressly allowed PPAs; that bill would have included private homes and smaller commercial systems. The issue was popular with legislators and the public and became a priority for many local governments during the 2013 legislative session.
Eventually this year Dominion agreed to a narrower bill as a temporary pilot project. In exchange, the bill gives Dominion legal certainty by prohibiting PPAs in its territory that fall outside the pilot project.
Other Virginia utilities refused to participate in the pilot program. As a result, the program and its rules apply only in Dominion Virginia Power’s service territory.
The pilot project will run for two years, after which Virginia regulators will evaluate it to determine whether it should be continued and expanded. The total size of all the systems installed under the legislation is capped at 50 megawatts. Although this is a tiny amount compared to states like New Jersey, which already has more than 1,000 megawatts of solar installed, it would mark a significant step forward for Virginia, which to date has installed less than 10 megawatts.
In addition to the 50 megawatts that can be installed under PPAs, another 30 megawatts of solar will be installed by Dominion itself under a program it refers to, somewhat confusingly, as “community solar.” Under that program, the utility plans to install and own solar systems on leased rooftops in select locations. The program includes no provision for selling the solar output to the building owners.
Wind systems also covered
The pilot project includes wind turbines as well as solar systems. Dominion’s service territory includes relatively few areas with wind resources good enough to make wind power economically attractive, but the Virginia Wind Center at James Madison University has been evaluating the possibilities under the pilot program and believes it may be useful for some customers interested in installing wind turbines.


![Sunday News: “Trump Is Briefed on Options for Striking Iran as Protests Continue”; “Trump and Vance Are Fanning the Flames. Again”; “Shooting death of [Renee Good] matters to all of us”; “Fascism or freedom? The choice is yours”](https://bluevirginia.us/wp-content/uploads/2026/01/montage011126.jpg)
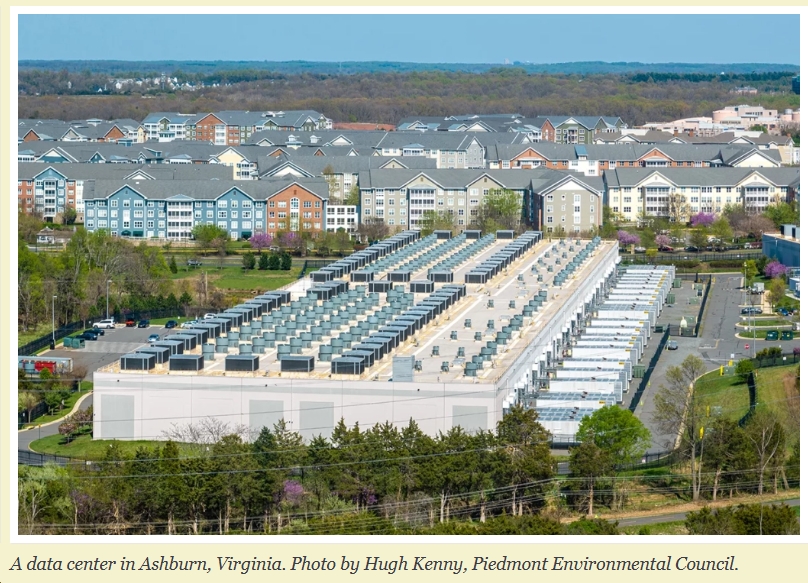
![VA DEQ: “pollution from data centers currently makes up a very small but growing percentage of the [NoVA] region’s most harmful air emissions, including CO, NOx and PM2.5”](https://bluevirginia.us/wp-content/uploads/2026/01/noxdatacenters.jpg)
![Thursday News: “Europe draws red line on Greenland after a year of trying to pacify Trump”; “ICE Agent Kills Woman, DHS Tells Obvious, Insane Lies About It”; “Trump’s DOJ sued Virginia. Our attorney general surrendered”; “Political domino effect hits Alexandria as Sen. Ebbin [to resign] to join Spanberger administration”](https://bluevirginia.us/wp-content/uploads/2026/01/montage010826.jpg)