by Ivy Main, cross posted from Power for the People VA
It’s a problem that divides communities and stymies lawmakers: Virginia’s transition to clean energy depends on building thousands of acres’ worth of large solar facilities, but a backlash from some rural neighbors makes siting projects increasingly difficult.
Most of the objections are aesthetic – few people prefer to look at rows of solar panels if they once enjoyed a bucolic country scene – but some opponents say they worry about the loss of farmland and trees. Solar, they fear, is bad for the land as well as the eyes. It doesn’t help that some early solar development suffered from corner-cutting that resulted in soil compaction and erosion. If that is solar, many people want no part of it.
In 2022, land conservation groups banded together with agriculture and logging interests to lobby for legislation requiring mitigation whenever a solar project would disturb more than 50 acres of forest or 10 acres of “prime agricultural soils.” House Bill 206 applies to any solar project developed under Virginia’s sort-of-streamlined “permit by rule” process, which is available to all but the largest facilities.
The solar industry initially fought the legislation, joined by some climate advocacy groups. They pointed out that no other industry is subject to mitigation requirements, and that solar provides greater climate benefits than forests and agriculture. Moreover, solar panels can be removed and the land returned to farming or forestry. By contrast, once land is converted to a housing subdivision or strip mall or data center, the damage is permanent.
Eventually the solar industry accepted compromise language that put off the effective date until the start of 2025 and gave industry members a voice in an advisory panel under the auspices of Virginia’s Department of Environmental Quality (DEQ). The law tasked this group with helping to develop “criteria to determine if a significant adverse impact to prime agricultural soils or forest lands is likely to occur as a result of a proposed solar project,” and if so, the actions that should be considered in any mitigation plan. DEQ was to use the working group’s conclusions to draw up regulations.
As it turned out, the working group agreed on very little. Its 717-page report found consensus on only a few points, leaving DEQ itself with the task of resolving key issues. On May 13, the agency published its proposed regulations. The regulations are currently under executive branch review, after which Interested parties and the public will have the opportunity to comment.
Meanwhile, a few things have happened since the passage of HB 206.
In March of 2022, DEQ toughened its stormwater regulations to address the runoff and erosion problems that had given solar a bad name in some communities. Building on that, the agency just released a new stormwater handbook that will become effective July 1, 2024, with sections specific to solar development.
Some solar industry members complain that DEQ’s stormwater regulations are unreasonably onerous, but no one questions the importance of preventing runoff and erosion. In any case, many companies are already using land-friendly practices that make it easier to meet tougher rules. One is the use of terrain following trackers, a technology that allows solar to be installed on uneven terrain instead of bringing in bulldozers to level the site. The trackers maximize solar production in hilly areas while preserving topsoil and vegetation.
The new tracker technology is among the suite of low-impact approaches gaining ground as the solar industry matures. DEQ encourages another eco-friendly practice: planting native species among and around solar arrays. Native plants provide food and habitat for insects whose numbers have plummeted in recent years, threatening our ecosystems. Though only a few solar projects have achieved DEQ’s pollinator-smart certification to date, most of the developers I’ve spoken with say they are open to it.
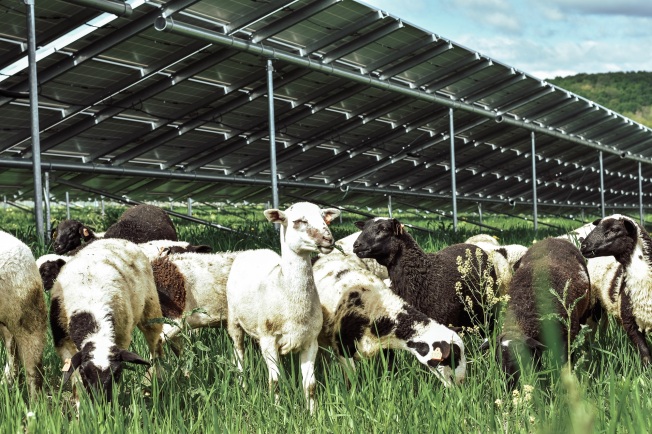

Gaining traction even faster is the practice of using grazing animals for vegetation management. Sheep hit the sweet spot: project owners save money they would have to spend on humans operating machinery, while the sheep thrive in the shade of solar panels and return nutrients to the soil. Already, 2% of sheep in the U.S. are being grazed under solar panels, according to an American Solar Grazing Association webinar, including at several large Virginia facilities providing power to Dominion Energy. Elsewhere, cattle graze under solar panels or crops grow between the rows, further erasing the distinction between solar facilities and agricultural use.
All-terrain trackers, topsoil preservation, native plants and incorporating active farming or grazing: all these practices ensure farmland isn’t “lost” to solar. Yet DEQ’s tougher stormwater rules, the solar industry’s increasingly land-friendly practices, and even the passage of HB 206 haven’t allayed concerns among solar opponents. Instead, rural counties have stepped up the pace of bans, caps and moratoriums.
One suspects the continued hostility isn’t because opponents lack familiarity with the ways solar can be eco-friendly, but because the opposition’s primary motivation isn’t preserving farmland. If what they really care about is keeping solar from cluttering up the viewshed (“preserving our rural heritage” is the euphemistic framing), then adding a new layer of mitigation requirements won’t change anything.
Admittedly, I never supported HB 206 in the first place. From an environmental perspective, solar is no worse for the land than monoculture pine plantations or commodity crops grown with pesticides and petroleum-based fertilizers. Done in a habitat-friendly way, solar can increase biodiversity and help heal the land. And solar addresses our CO2 problem, far more even than trees.
Still, DEQ’s job was to try to find a middle ground between the solar industry and its detractors, and in fairness, their effort gets some things right. The proposed rules recognize that there are degrees of impact a solar facility can have, and that practices like leaving topsoil undisturbed or incorporating agrivoltaics should be rewarded with lower mitigation requirements. A neat table delineates the various levels of impact and proposes differing levels of mitigation to match. Mitigation mostly takes the form of land set-asides, but can also be satisfied with per-acre payments.
And yet the proposal misses the mark on at least three fronts. First, it fails to give full credit to solar projects that minimize soil disturbance and incorporate agrivoltaics. DEQ should recognize that adopting best practices is itself mitigation, which should obviate the need for land set-asides or monetary payments.
Second, the proposed regulations make no exceptions for projects owned and operated by local farmers who incorporate solar into their farm activities in order to increase and diversify their income without having to sell their land. If the point of HB 206 was to protect farming, DEQ has shot wide of the mark.
Finally, the dollar amounts that DEQ proposes in lieu of land set-asides are punishingly high, with perverse effects. A solar company that has to pay a stiff penalty must pass that cost along in the form of a higher price for the electricity produced. If a utility has to pay more for electricity, ratepayers ultimately foot the bill.
The alternative is equally counterproductive. I noted at the start that DEQ’s permit-by-rule process is available to all but the largest projects, but it is not the only pathway open to developers. Projects over 150 MW are required to go to the SCC for approval, but smaller projects aren’t foreclosed from doing so. If DEQ makes its own process too onerous, solar developers will go to the SCC instead. The SCC requires that a developer secure a local permit, but not that it employ soil-saving practices, agrivoltaics or mitigation.
It would be great if DEQ could turn the lemon that is HB 206 into a lemonade of a solar industry adopting eco-friendly development practices and incorporating pollinator plantings, sheep grazing, and other agrivoltaic businesses. What we have instead is a proposal that may kill the permit-by-rule program without producing any benefit to anyone – in effect, turning lemonade into lemons.
There is still time to get it right. DEQ may not be able to resolve the solar wars, but a good set of regulations would position Virginia to make the most of a solar industry that is essential to our future.
This article was originally published in the Virginia Mercury on June 12, 2024.



![Sunday News: Hurricane Melissa Could Be Devastating; Trump ILLEGALLY Raises Tariffs on Canada; “East Wing rubble mirrors the demolition of America”; “How Did [VA] Become the Data Center Capital of the World?”; “Western Va. congressmen silent on Trump’s demand taxpayers pay him $230 million”](https://bluevirginia.us/wp-content/uploads/2025/10/montage1026-238x178.jpg)





![Sunday News: Hurricane Melissa Could Be Devastating; Trump ILLEGALLY Raises Tariffs on Canada; “East Wing rubble mirrors the demolition of America”; “How Did [VA] Become the Data Center Capital of the World?”; “Western Va. congressmen silent on Trump’s demand taxpayers pay him $230 million”](https://bluevirginia.us/wp-content/uploads/2025/10/montage1026-100x75.jpg)
